PREVENTION: A medical expert discusses factors associated with the onset of a disease that affects millions worldwide annually…
By Joseph Kim
LEXINGTON, US —Liver cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer death in the United States and the seventh among South African men and women.
The most common type of liver cancer in adults is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and men are more likely to develop HCC than women.
According to a 2022 journal article, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the number of new liver cancer cases per year will increase by 55 percent between 2020 and 2040. This could result in 1.4 million people being diagnosed with liver cancer in 2040.
The incidence and mortality of liver cancer cases in Africa represent 7.8 and 8.1 percent of the global cases, according to the latest Global Cancer Statistics (GLOBOCAN 2020).
Primary liver cancer in South Africa is a public health concern, and currently the seventh leading cause of death among SA men and women after colon cancer, according to GLOBOCAN 2018. Despite this, publications of this disease reportedly remains scarce, if not absent.
It typically develops in people with long-lasting liver disease caused by hepatitis virus infection or cirrhosis. In many cases, liver cancer is a preventable cancer, so raising awareness about prevention is important.
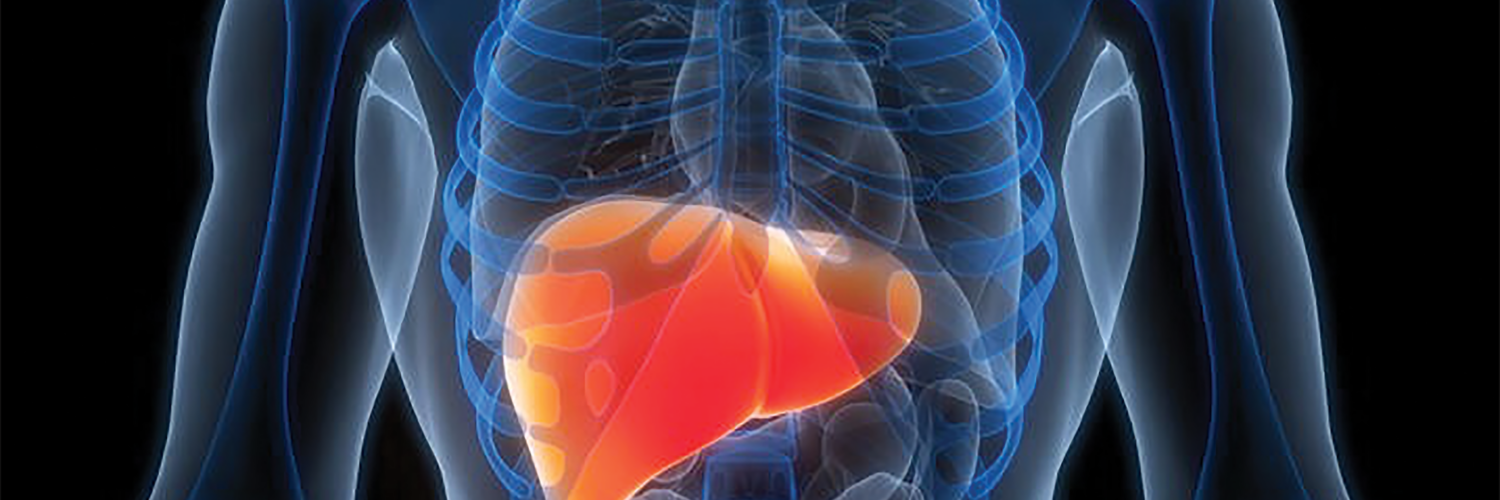
Primary liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver. Cancer that forms in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver is not primary liver cancer. The liver is one of the largest organs in the body. It has two lobes and fills the upper right side of the abdomen inside the rib cage.
The main functions of the liver include making bile to help digest fat that comes from food; storing glycogen (sugar), which the body uses for energy; and filtering harmful substances from the blood so they can be passed from the body in stools and urine.
Types of liver cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma and bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) are the main types of adult primary liver cancer.
Most adult primary liver cancers are hepatocellular carcinomas. This type of liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
Primary liver cancer can occur in both adults and children. However, treatment for children is different than treatment for adults.
Signs and symptoms of liver cancer
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by adult primary liver cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
• a hard lump on the right side just below the rib cage
• discomfort in the upper abdomen on the right side
• a swollen abdomen
• pain near the right shoulder blade or in the back
• jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes)
• easy bruising or bleeding
• unusual tiredness or weakness
• nausea and vomiting
• loss of appetite or feelings of fullness after eating a small meal
• weight loss for no known reason
• pale, chalky bowel movements and dark urine; and
• fever
How can I prevent liver cancer?
There are a few steps you can take that research has shown can reduce your risk of liver cancer.
Get the hepatitis B vaccine: The hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Many infected people don’t experience any symptoms until decades later, when the disease has progressed. It’s often called the “silent epidemic” for this reason.
Most people get a vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection when they’re newborns. Research has shown that this vaccination lowers the risk of liver cancer in children. It is not known yet if this vaccination also lowers the risk of liver cancer in adults. The vaccine is also available to adults in a different dosage.
Get treatment for chronic Hepatitis B infection: The treatment for chronic HBV infection can include interferon and nucleos(t)ide analog therapy. These two treatments may reduce your risk of developing liver cancer.
Preventing the spread of hepatitis C: There is no vaccine for HCV, but there are treatments that can cure most people. Most new infections progress to long-term infections.
The best way to prevent HCV is by avoiding behaviours that can spread the disease, like sharing needles or syringes, engaging in sexual activity with a person who’s infected with HCV or getting unregulated tattoos or body piercings.
Testing is the first step to know more about your health. If you have HCV, talk to your doctor right away to start treatment.
Maintaining a healthy liver: Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver and can be caused by hepatitis or chronic alcoholism. The damage generally can’t be undone, but, if caught early, can by treated and further damage can be limited.
Moderating alcohol use: Cirrhosis caused by heavy alcohol use is a risk factor for liver cancer. Liver cancer can also occur in heavy alcohol users who do not have cirrhosis.
People who are heavy alcohol users with cirrhosis are 10 times more likely to develop liver cancer than heavy alcohol users who do not have cirrhosis.
Quit smoking: In addition to alcohol use, cigarette smoking has been linked to a higher risk of liver cancer. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the number of years the person has smoked.
If you have any questions about your current risk factors for liver cancer, talk to your primary care physician about your options.
* The writer, Dr Joseph Kim, is a surgical oncologist at the University of Kentucky. Additional reporting by WSAM reporters